Human Digestive System 1
Human body requires energy to perform Metabolic Activities, the food we ate provides us energy to body, Human Digestive System digest this food to provide us energy . Human digestive System digest the food in stomach our food contain following component
1) Carbohydrates
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbohydrate
2) Protein
3) Fat
4) Minerals
5) Vitamin
Human Digestive System –
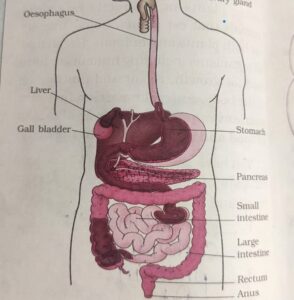
Human digestive consist of the following –
1) Alimentary Canal
2) Digestive Glands
Alimentary Canal –
Alimentary Canal begins with Mouth and ends with Anus
Mouth –
It helps to taking food in
it leads to Buccal Cavity
it consist Salivary Glands
Salivary Glands –
Salivary Gland –
There are 3 Pairs of Salivary Gland –
1) Parotids – Place- Cheeks
These are The Largest Salivary Gland
The Parotid Ducts open Near the Upper Second Molar Teeth
The Parotid Duct is also Known Stensens Duct
Mumps – It is the Viral infection of Parotid Gland , the Glands are Swell in this Disease with Pain
2) Sub- Maxillary/ Sub – Mandibular – Place- lower Jaw
The Sub maxillary Duct is Also Known as Whartons Duct
3) Sub – Lingual – Place- Below the Tongue
The Sublingual Duct also Known as Duct Of Rivinus
Neet Topic wise Questions – Animal Classification 1
Teeth –
Thecodont – The Embedded Attachment of tooth in a Socket of Jaw bone is called Thecodont
Diphyodont – Organisms having 2 sets of Teeth as Milk Teeth and Permanent Teeth During their life this type of Dentition is called Diphyodont
Milk Teeth –
Humans bear 2 Sets of Teeth in Their Lifetime
The 1st set of Teeth begins to to Appear after 6 month or so and fall off between 6 to 8 year of age
These teeth are called Milk Teeth and they are Temporary
There are 20 milk Teeth 10 in each Jaw
Permanent Teeth –
The Milk Teeth are Replaced by Permanent Teeth
The Permanent Teeth are 32 in number
16 in each Jaw
As follows –
28 – permanent teeth complete at the age of 18 year
4 – Molar are added after age of 18 year
Wisdom Teeth – it is the 3rd Molar in adult referred as Wisdom Teeth
Tooth Decay –
Also Known as Dental Caries
● Plaque – it is a Yellow film that develops naturally on the teeth and it contains bacteria and food components , it can be removed by proper brushing
● But sometimes we do not brush after eating and the bacteria goes increase and accumulate in the Plaque
● The bacteria in the Plaque Convert sugar of food into acid
● Acid Dissolved Enamel and Damage the tooth this is Known as Tooth Decay
- It occurs when Bacteria ( Streptococcus Mutans ) grows on remaining food particles especially sugar that is attached to the teeth and Produce acid
- This acid act on the tooth and cause softening or Demineralisation of enamel and dentine .
The Bacteria colony grows in size and forms Dental PlaquesTongue –
It is a Fleshy Muscular Organ
It is attached at the back and Free at the Front
It can be Moved in all directions
Function –
– It help in mixing the chewed food with saliva
– Help in Swallowing
– Help to detect different tastes of food with the help of Taste Bud
The surface of tongue is not smooth it is rough due to presence of large number of tiny bumps known as taste buds
These buds detect different tastes of food
The structure of all the taste buds are Identical
The Taste bud detect the Following 4 Taste
1) Sweet
2) Salty
3) Sour
4) Bitter
These taste can be identified in different areas of the Surface of Tongue
● Papillae – The Surface of the Tongue has Small Projection called as Papillae
It bears some taste buds

Neet Topic wise Questions – Animal Classification 1
Oesophagus ( Food Pipe) –
The Tongue Push the food from the Mouth towards the Pharynx
Pharynx – it is the Common Passage for Food & Air
Bolus – The Moist Ball of Food is known as bolus
Function –
The Main function of the Oesophagus ( Food PIPE) is to Transfer the food from the Pharynx to the Stomach , the length of the Human Oesophagus is almost 25 cm long and it is Muscular Tube . The wall of the Oesophagus is Muscular in nature , the food pipe runs along with the Neck and Chest. The Oesophagus and the and the Trachea ( Wind Pipe ) opens into the Pharynx. A Cartilaginous Flap called Epiglottis Prevent the Entry of the Food Into the Glottis during Swallowing. The Oesophagus did not get involved in the Process of the Digestion the food is pushed down by movement of the wall of the oesophagus this movement happens throughout the alimentary canal and it pushes the food down to the stomach.
Stomach –
It is the Thick walled Flattened Bag Present in the Upper Abdomen
It is the Widest Part of the Alimentary Canal and Receives food From The Food Pipe
The Inner Lining Of The Stomach Secretes Following –
1) Mucus
2) Hydrochloric Acid
3) Digestive Juices
Mucus – it protects the Inner Lining Of the Stomach
Hydrochloric Acid –
It Kills the Bacteria which Enter Along with the food and also it makes the Medium Acidic so the Digestive Juice can Act
Digestive Juice – it help to breakdown the Protein into Simpler Substance
Small Intestine –
It is the Longest part of the alimentary canal
It is about 6- 7.5 Meter Long tube
The digestion and assimilation and absorption of food occurs here
The length of small intestine varies in different Organisms depending Upon the type of Food they ate
Small intestine is longer in herbivorous animal because of Cellulose they ate
Small intestine is shorter in carnivorous because Meat is easy to digest
Small Intestine consist of Following –
a) Duodenum – It is the initial Part of the Small Intestine
– It is C shaped in Structure
– The bile and Pancreatic Ducts open here
b) Jejunum – it is the Part next to Duodenum
It is a short region of small intestine
c) Ileum – it is the Longest part of the small Intestine
Villi – the Internal wall of the Small Intestine is Provided with Long Finger like Projections known as Villi
The Villi increase the Surface area & enhanced absorption Capacity
At the base of Villi there is intestinal glands with secret digestive enzyme for digestion of protein carbohydrate and fats
The digestion in small intestine is carried out with the help of
1) Secretion from The liver and Pancreas
2) Digestive Juices Secreted by Small Intestine
Large Intestine –
Large Intestine –
It is about 1.5 meter Long
It is divided into following 3 Parts
1) Caecum
2) Colon
3) Rectum
1) Caecum –
It is a Point where the Ileum Joins the Large Intestine, a Sac – Like Part Caecum is Present
It is a Small Pouch Situated at Junction of The Small and Large Intestine
From the End of the Caecum a Finger Like Structure ( Worm Shaped ) is present Known as Vermiform Appendix ( When it Inflamed it Causes Appendicitis)
2) Colon – The Caecum Opens into Colon
The colon is divided into three parts
1) An Ascending
2) A Transverse
3) A Descending – it Opens into Rectum
3) Rectum – it is about 15 Cm long
It Opens into Anus
It stored the Semi Solid Faeces
● Anus – the Faecal matter Passes out through the Anus

